
Simon Wren-Lewis
This post is inspired by another, by Jan-Werner Müller. I have talked about Müller’s ideas on populism before. This particular post is a plea to focus less on the voters who elect populist politicians, and more on the politicians themselves. He writes:
In 2010, Viktor Orbán did not campaign on a promise to draft a new constitution, weaken checks and balances, and radically reduce media pluralism. Instead, he presented himself as a competent mainstream Christian Democrat. In Poland, the Law and Justice (PiS) party went out of its way to stress its character as a reasonable conservative party which simply wanted to provide more benefits to families with children.
The idea that most voters should see beyond the mask to understand who politicians really are is ridiculous. As the 2016 US general election showed, the information content of the broadcast media can be increasingly small.
Does Trump provide a counterexample of this, because he was an ‘outsider’ who was elected? I would say no for two reasons. First, the Republican Party had played a large part in creating the political environment that allowed his populism to win votes. Second, the Republican Party seems quite content to behave in ways which complement Trump’s authoritarianism (by attacking the CBO, for example).
The message is that if you want to investigate populist regimes (using populist in the Müller sense) you need to look at political elites rather than the electorate. I think he is right. But what makes an elite adopt an authoritarian path? I am sure there are many answers to that question, but what I will try to do below (in no doubt a very ‘untutored’ way) is to show one route in which a formerly pluralistic democracy can be moved in a populist, authoritarian direction by elites from the right. I’m an economist, so I use a simple model.
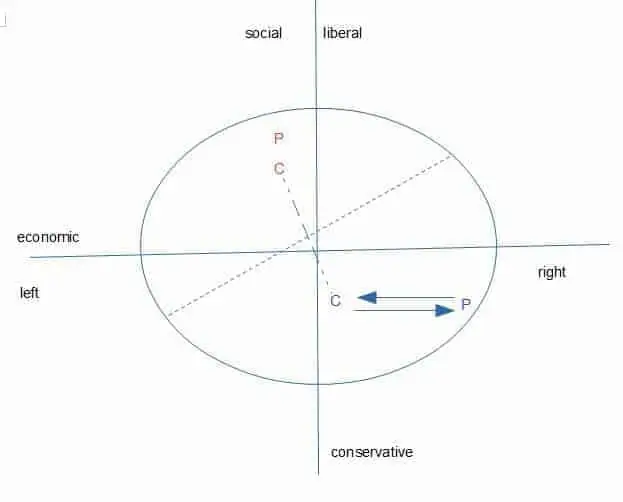
Here is a two dimensional variation on the familiar left-right diagram. The additional dimension is sometimes called ‘identity’ or ‘culture’. Let us assume that voters are evenly distributed inside the circle (not necessarily a good assumption: see here). In a two party system you might expect both parties, if their main concern was to be elected, to adopt positions that put them close to the centre. This is because the party a voter will vote for is governed by the party that is nearest to them.
But suppose that a party wants to take a less centrist position, either because its backers wish this or because its politicians believe in some ideology. To be concrete, suppose the party of the right wants to adopt a very right wing economic policy that involves, for example, distributing income from most people to the very rich. In a one-dimensional left-right space such a party would be doomed. But suppose their opponents, for whatever reason, were fairly liberal. If we assume that the left is fairly moderate on economic issues, then that places the two parties at the position given by P in the diagram above. That leaves them evenly matched (to see why, see below).
The party on the right will want to focus on their socially conservative platform, while the party on the left will stress their more ‘moderate’ economic platform. This looks like a stable situation, which contains no threat to a pluralistic democracy. What could change to upset it? Here is just one possible route.
If the right has more influence on the media than the left, they can campaign on a platform that differs from the platform they intend to implement. If you can pretend that you are a moderate party on economic issues rather than an extreme right party, and this pretense works, then your party wins. So in terms of voter perception, the party on the right moves along the upper arrow from position P to C. The left party might respond in kind by pretending they are less liberal than they are, but because they have less media influence they cannot move so far from their true position. If we look at the campaign positions of the two parties, marked by C, it is intuitively clear that the right wing party wins any election. The dotted lines show a proof: to see which party wins (assuming my geometry is correct), draw a line between the two positions, and then draw a line at right angles that bisects it. Every voter on that line is indifferent (equidistant) between the two parties, and therefore every voter either side of the line votes for each party.
We see this in the US with tax cuts (pushing the idea that lower corporation taxes will mainly raise wages), in the UK with austerity (which was really a policy to shrink the state much further than most wanted, dressed up as some kind of moralistic injunction that governments should be like households) and especially Brexit, where advocates pretended there would be no economic cost to leaving the EU. The counterpart of hiding a right wing position is to emphasise conservative issues. This is most obvious with the culture war in the US, together with the politics of race. In the UK the key social issue was immigration, which the Conservatives started focusing on from the late 1990s (the great thing about immigration as an issue for the right is that it can be (falsely) given an economic dimension). Again Brexit is an exemplar, with not just immigration (‘protect our borders’) but nationalism (‘take back control’).
While this results in short term gains for the right, as a tactic it is unstable in the longer term because governments once in power implement their real economic policies. We will move back from C to P on the lower arrow. Voters observe tax cuts for the better off at their expense, they observe the impact of austerity and, in the UK, they observe the consequences of Brexit. It may take some time, but right wing leaders know they are vulnerable to reality winning out over spin, so they may wish to take actions to offset the democratic consequences of being found out.
There are lots of directions this authoritarian turn can take. Taking greater control of the media, either directly by shutting down critical media or buying off media owners in exchange for support, is one direction we see taken in Hungary. Gerrymandering is favoured by Republicans in the US. Portraying opposition leaders as traitors is favoured in the UK. Ramping up nationalism and the ‘threat’ from immigration almost everywhere.
Politics that is exclusively along the social conservative/liberal axis can degenerate into a kind of identity politics where you just vote for your tribe. As Müller writes:
The problem starts when citizens view every issue purely as a matter of partisan identity, so that the credibility of climate science, for example, depends on whether one is a Republican or a Democrat. It gets worse when partisan identity becomes so strong that no arguments from or about the legitimacy of the other side ever get through.
The path to authoritarianism I set out here is not meant to be the whole story, and is not meant to correspond with any particular country. What I hope it does illustrate is how an authoritarian government can emerge when a party adopts a very right wing economic policy, and pretends it has not. It happens without voters changing their views or preferences in any way. It is authoritarian populism that comes from the behaviour of right wing elites.
The post originally appeared on Mainly Macro.
Simon Wren-Lewis is Professor of Economics at Oxford University.