Few would consider Italy—known for its ‘macho’ politics and far-right leaders promoting ‘traditional’ gender roles—as a hotspot for feminist values in Europe. But a new survey, conducted in late 2020 and released yesterday, suggests this may be changing.
Of the eight European countries included in the survey, which had 12,000 respondents, people in Italy were the least likely to blame feminism for men’s feelings of marginalisation and demonisation.
Meanwhile, in Sweden—long seen as a bastion of progressive gender-equality politics—more people (41 per cent) than anywhere else surveyed said they at least somewhat agreed with the statement: ‘It is feminism’s fault that some men feel at the margins of society and demonised.’
Daniel Poohl, editor-in-chief with the Swedish anti-extremism group Expo, told openDemocracy that ‘the surprising anti-feminist views of Swedes’ could be partly explained as a backlash to successful feminist movements. ‘Some victories of Swedish feminism in the last years could have activated the rise of strong opposite attitudes,’ he said.
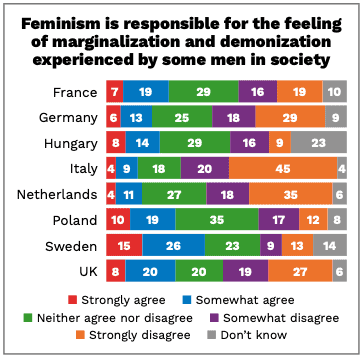
After Sweden, about 30 per cent of participants in Poland expressed anti-feminist views, followed by the United Kingdom (28 per cent), France (26 per cent), Hungary (22 per cent), Germany (19 per cent) and the Netherlands (15 per cent). Only 13 per cent of Italian respondents, however, expressed such views and 65 per cent said they either strongly or somewhat disagreed with them.
Simone Rafael from the Amadeu Antonio Foundation in Germany, which commissioned the research along with Expo and HOPE not Hate in the UK, called the scale of anti-feminist opinion in Europe ‘very worrying’. Nick Lowles, chief executive of HOPE not Hate, added that, in many countries, an ‘anti-feminism agenda’ is now ‘wrapped up in the growing right-wing cultural wars which is much more aggressive, quite violent rhetoric and is used particularly by younger men’.
‘State of hate’
The anti-extremism groups’ survey was commissioned as part of a new report entitled ‘State of Hate: far-right extremism in Europe’. It also revealed that at least a quarter of the survey’s respondents said they had negative feelings towards Muslim people. Almost a third reflected hostile views towards immigrants generally and more than a third reflected such views of Roma people.
‘This report shows that the threat against democracy is changing form and strategy. The far right of today is a transnational movement that organises supporters through networks rather than old-fashioned organisations,’ said Poohl.
Ahead of the 2019 European Parliament elections, openDemocracy uncovered how a dozen US Christian right ‘fundamentalist’ groups had poured at least $50 million of dark money into Europe over a decade, boosting the far right that was angling for record wins that year. Lowles said extremist ideologies were now ‘internationalised like never before’—and ‘resistance must be so, too’.
According to the survey, the majority of respondents in Hungary hold negative views towards immigrants (60 per cent) and Muslim people (54 per cent). These numbers are about twice as high as they are in the UK, where 30 per cent hold such views of immigrants and 26 per cent of Muslims.
When asked if they sympathised with Black Lives Matter protests against racism and discrimination against minorities, most respondents in Germany (52 per cent), Sweden (51 per cent) and the UK (51 per cent) said they did. This was not the case in any of the other countries surveyed.
‘Deep mistrust’ of authorities
The report also highlighted a ‘deep well of mistrust’ in authorities, adding that populists and extremists across Europe could attempt to exploit such an environment.
Political disenchantment was particularly pronounced in Italy and France, with 79 per cent and 67 per cent of respondents respectively saying that they thought their political system was wholly or partially broken. These figures were also high in Poland (63 per cent), the UK (58 per cent) and Hungary (55 per cent).
‘Europe’s far-right and anti-democratic scene is connected in many ways nowadays—it is anti-Semitism, Islamophobia and white-supremacy thinking that the far-right enemies of democracy agree on,’ concluded Anetta Kahane, chair of the Amadeu Antonio Foundation. This report, she argued, ‘makes the commonalities visible that we must fight together to protect democracy and human rights in Europe.’
This article was originally published on opendemocracy.net
Tatev Hovhannisyan is Eurasia investigations fellow with OpenDemocracy. Previously she was an editor at the Mediamax news agency and CivilNet TV in Armenia. She has also contributed to the Guardian, Mother Jones, BBC Russia, Voice of America and Radio Free Europe / Radio Liberty.

